클래스는 객체들의 공통점을 찾아내서 하나의 틀로 만든것이다.
클래스 구조

# 클래스 안에있는 변수를 멤버 변수라고 한다.
# 클래스 안에있는 함수를 멤버 메소드라고 한다.
이전에 함수를 만들고 호출하기전에 Func f = new Func( ) 를 먼저 작성했는데
이것이 바로 객체를 선언한것이다.
# 클래스를 메모리에 올려준 상태를 객체라고 한다.
전자제품들을 나타내는 클래스를 만들어보자.
# 클래스는 DB의 테이블을 만든다는 느낌으로 만들면 쉽게 만들수있다.
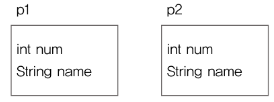
먼저 Product 라는 이름의 클래스를 만들어보자.
public class Product {
int num;
String name;
}
그 후, ProductMain 이라는 이름의 메인함수가 포함된 클래스를 만들자.
public class ProductMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Product p1 = new Product();
p1.num = 1;
p1.name = "computer";
Product p2 = new Product();
p2.num = 2;
p2.name = "oven";
System.out.println(p1.num);
System.out.println(p1.name);
}
}# 클래스를 메모리에 올려야 사용할수있다.
# 이렇게 메모리에(heap) 올라온상태를 객체라고 한다. (instance, Object)
아래와 같은 데이터를 처리하고자 하는 클래스를 만들어보자.

클래스안에 필요한 멤버변수를 만든다.
public class Student {
String name;
int kor;
int eng;
int math;
int total;
double avg;
}
그 후 메인함수에 Student 클래스의 객체를 만든 후 데이터를 저장한다.
public class StudentMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Student s1 = new Student();
Student s2 = new Student();
Student s3 = new Student();
s1.name = "Student_A";
s1.kor = 90;
s1.eng = 80;
s1.math = 100;
s1.total = s1.kor + s1.eng + s1.math;
s1.avg = s1.total / 3;
s2.name = "Student_B";
s2.kor = 90;
s2.eng = 95;
s2.math = 100;
s2.total = s2.kor + s2.eng + s2.math;
s2.avg = s2.total / 3;
s3.name = "Student_C";
s3.kor = 80;
s3.eng = 90;
s3.math = 70;
s2.total = s2.kor + s2.eng + s2.math;
s2.avg = s2.total / 3;
System.out.println(s2.name);
System.out.println(s2.kor);
System.out.println(s2.eng);
System.out.println(s2.math);
System.out.println(s2.total);
System.out.println(s2.avg);
}
}
s3의 영어점수를 88로 변경해보자
s3.eng = 88;
s3.total = s3.kor + s3.eng + s3.math;
s3.avg = (double) s3.total / 3;
System.out.println(s3.name);
System.out.println(s3.kor);
System.out.println(s3.eng);
System.out.println(s3.math);
System.out.println(s3.total);
System.out.println(s3.avg);# 영어점수만 바뀌며 총합과 평균은 메모리에 저장되있는것일뿐 바뀌지 않는다.
# 변수 앞에 (double)을 붙여서 데이터타입을 double로 만들어줬다.
total변수와 avg변수를 한번에 계산해서 저장해주는 함수를 만들어준다.
public class Student {
String name;
int kor;
int eng;
int math;
int total;
double avg;
void calculate() {
total = kor + eng + math;
avg = (double) total / 3;
}
}# return이없는 void함수를 사용한다.
# 같은 클래스속의 함수에서는 클래스의 멤버변수를 마음대로 가져다 쓸수있다.
이제 메인클래스에서 calculate 함수를 사용해보자
Student s2 = new Student();
s2.name = "Student_B";
s2.kor = 90;
s2.eng = 95;
s2.math = 100;
s2.calculate();
System.out.println(s2.name);
System.out.println(s2.kor);
System.out.println(s2.eng);
System.out.println(s2.math);
System.out.println(s2.total);
System.out.println(s2.avg);
영어점수를 79점으로 변경한다.
s2.eng = 79;
s2.calculate();
System.out.println(s2.name);
System.out.println(s2.kor);
System.out.println(s2.eng);
System.out.println(s2.math);
System.out.println(s2.total);
System.out.println(s2.avg);# 이제 총합과 평균도 변경된다.
스튜던트 클래스에서 멤버변수의 값을 출력하는 클래스의 멤버메소드를 만들자
void print() {
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(kor);
System.out.println(eng);
System.out.println(math);
System.out.println(total);
System.out.println(avg);
}
'Java' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Java] 메소드 오버로딩(Method Overloading) (0) | 2022.07.01 |
|---|---|
| [Java] 메모리 구성과 Static (0) | 2022.07.01 |
| [Java] 함수 (0) | 2022.07.01 |
| [Java] 배열(Array), length (0) | 2022.07.01 |
| [Java] Java와 기본 식: 데이터타입, 조건문, case, 반복문 (0) | 2022.06.30 |



댓글